There is no doubt that given the juggernaut of the 1942 Japanese Army and Navy expeditions the Battle of Midway and the Guadalcanal Campaign were turning points in the war – each in their own different way. There is no shortage of books and online sources that can offer outstanding detail, commentary and analysis of the importance of Midway and Guadalcanal. But there are other events in the war that shaped the strategic and tactical vision of the Japanese military from the Spring of 1944 until the end of the war. The lessons learned from these events shaped the Japanese plan Ketsu-Go, the defense of the main home islands against allied invasion. The events were the Battle of Biak Island, Peleliu, the Battle of Philippine Sea, and the air Battle of Formosa.
The Battle of Biak
Most people have never heard of the Battle of Biak Island. Biak is not a large island. It is 45 miles long and 23 miles wide – about the size of the Hawaiian island of Moloka‘i. It is located near the western end of New Guinea and is part of the modern Indonesian Province of Papua. For reasons important to General Douglas MacArthur’s Southwest Pacific command, its capture was planned as a one week operation in late May 1944. The goal was to secure the “next island” in the overall advance that could support an airfield and extend MacArthur’s land-based air cover for scouting and operations.
The Southwest Pacific Command ran a separate intelligence operation from that of Admiral Nimitz’s Central Pacific Command. It was not that they did not share intelligence, but MacArthur preferred his own council – and his experience on intelligence was that it grossly overestimated or underestimated Japanese resistance or the suitability of the next step in the campaign to provide a locale for constructing a suitable airfield. This was his experience with intelligence reports associated with the campaigns of Hollandia and Atape, both of which failed to provide suitable ground for building an army air force base. The intelligence on Biak grossly underestimated the size of the Japanese garrison and its pre-invasion disposition.
MacArthur’s attitude towards his own Intelligence Operation will come to the fore during discussions of the 1945 amphibious landings on the home Japanese islands.
In early 1944 at the Battle of Sio on New Guinea, Australian troops recovered a complete set of Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) code books and ciphers. Nonetheless, MacArthur’s “code breakers” missed communications indicating that the IJA had moved the 41st Division’s 222nd Infantry Regiment, an elite, battle-hardened and well-trained group to Biak just before the invasion. Because of an over reliance on aerial surveillance, the allies downplayed information that would have indicated efforts and materials to fortify caves and ridges inland, not the beaches—contrary to standard Japanese tactics, and contrary to Allied expectations.
Allied planners envisaged a week-long operation based on intelligence that there were approximately 2,000 Japanese troops defending the island. In fact, the Japanese garrison was 11,000-12,000 troops.
Based on an appreciation of the Allied objectives (capturing the already built and operational airfields), island commander Colonel Kuzume Naoyuki focused his defensive plans away from the water’s edge. His plan was to let the Americans come ashore unopposed so that they would advance into the trap he had prepared for them utilizing a series of caves that were located west of Mokmer air field and to the east of Bosnek airfield. This defensive complex was intended to turn the area around the airfields into a honeycomb of defended caves and pillboxes filled with riflemen, automatic weapons, artillery, batteries of mortars, and a single company of light tanks. The western caves were connected by a series of underground tunnels that were constructed for fighting purposes. Kuzume also stockpiled these positions with ammunition, food, water, and other supplies, with several supply depots located around the eastern cave area, along with living quarters for the defenders. Water was limited on Biak and had to be strictly rationed by the US troops. Heat and humidity would take a heavy toll during the fighting.
Kuzume had no expectations other than he and his fighting force would ultimately be defeated but he carried out his orders as he well understood the larger objectives of inflicting casualties to weaken the will of the allied war fighters and the public back home.
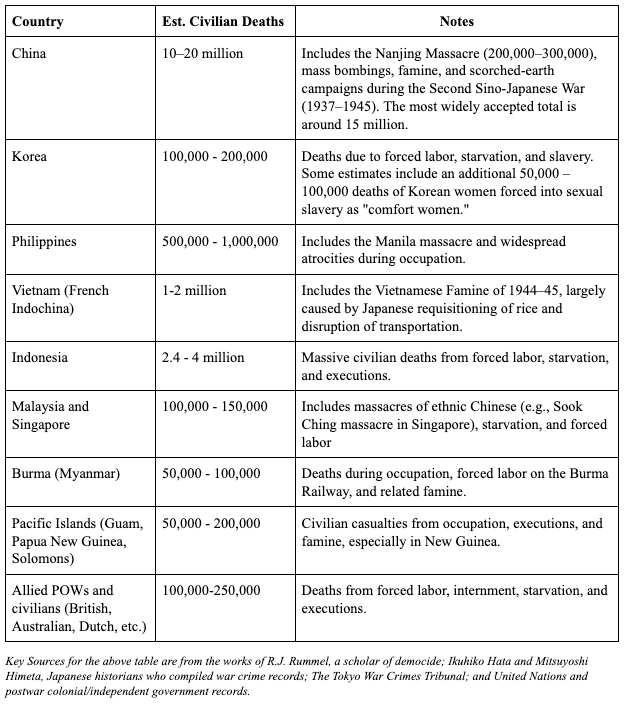
Many online sources are available to provide the details of fighting on the island. Combat began with the May 27, 1944 landings and continued until June 22nd which marked the end of all organized resistance. Some 3,000 Japanese remained on the island attempting guerrilla-style warfare to no particularly successful end. At the end of the campaign (late July) virtually all Japanese had died in combat or from disease and/or starvation. Allied losses were 460 killed in action with 2,440 additional non-lethal casualties the majority of which were disease related. Some 600 British Indian and Javanese forced laborers were also rescued.
Reports from Colonel Kuzume that reached IJA headquarters indicated that the strategic objectives of extracting mounting Allied casualties was a good strategy in the face of overwhelming allied ground forces, equipment, logistics support, air superiority, and control of the waters around Biak by allied naval forces. This strategy was implemented and faced the allied invasions of Peleliu (the Palau Islands) and the battles of Iwo Jima and especially Okinawa. They were intended – and we understood them to be harbingers of what awaited any attempted invasion of the Japanese home islands. In a different form, the same strategy was implemented at Leyte and Luzon in the Philippine Islands: unopposed landings with interior defenses in place to extract maximum allied casualties.
Peleliu
There is and will ever be controversy on the need to invade and secure Peleliu instead of bypassing the island to let its defenders “wither on the vine.” That is a topic for another post. For purposes of this series, Peleliu is important in that it exemplifies the changing strategy of the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) in island invasions following the campaign on Biak.
The planners predicted that the island would be secured within four days. But IJA plans were that instead of defending the beaches, they focused on fortified inland positions, allowing U.S. forces to land relatively unopposed and then drawing them into a kill zone. It was a plan similar to Biak, but the terrain on Peleliu was radically different – more akin to that of Iwo Jima and Okinawa. The island’s central highlands (Umurbrogol ridges) became the core of Japanese defense. The coral ridges were honeycombed with over 500 caves, interconnected by tunnels that allowed troops to move, reinforce, and resupply without surfacing. Positions included machine gun nests, mortar pits, anti-aircraft guns, and artillery camouflaged and embedded into the ridges. Many caves had steel doors and ventilation, enabling troops to survive prolonged bombardments. The “four day” operation began on 15 September 1944 and lasted until 27 November 1944 when the island was declared secure. Nonetheless the Army’s 81st Infantry Division remained engaged on the island until the end of organized Japanese resistance on 18 January 1945. Even then, a Japanese lieutenant with 26 infantry soldiers and 8 sailors held out in the caves on Peleliu until 22 April 1947, only surrendering after a former Japanese admiral convinced them the war was over.
The heavily outnumbered Japanese defenders put up stiff resistance, 98% fighting to the death in the name of the Japanese Emperor. The island became known in Japanese as the “Emperor’s Island” and held up as an example of the true spirit of the Japanese fighting forces.
The 1st Marine Division, the “Old Breed”, suffered a KIA and casualty rate that was unmatched among Allied forces during the war. When the men of the Army 81st Infantry Division relieved the “Old Breed” they saw men stumbling forward, their eyes sunken and glazed over with what became known as the “2,000 yard stare”, moving forward like zombies. Episodes 6 and 7 of the mini-series, “The Pacific” capture this experience. After the battle, Russel David, a private in the First Marines wrote about his experience of battle on Peleliu.
“I picked up the rifle of a dead marine and I went up the hill. I didn’t worry about death anymore. I’d resigned from the human race. I only wanted to be as far forward as any man when my turn came, As a fighting outfit the First Marines was finished. We were no longer human beings. I fired at anything that moved in front of me, friend or foe. I had no friends. I just wanted to kill.”
On 24 November the Japanese force commander radioed Tokyo, “Our sword is broken and we have run out of spears”. He then burnt his regimental colors and performed ritual suicide. Prior to that IJA headquarter had been well informed about the “success” of the Peleliu strategy as a lethal strategy against any invasion of the home islands.
The Battles of Philippine Sea and Formosa
While the name might indicate a ship-to-ship engagement, the first two days of the conflict were fought in the skies in the area of the Marianas Islands. Just a few weeks after the start of the Biak landings, the massive Task Force 58 under the command of Admiral Raymond Spruance, began landings on Saipan. The importance of Saipan is covered in a later post focused on that battle. In short, were the allies to capture Saipan and neighboring Tinian, the Army Air Force B-29 Superfortress bombers would be in range of the main Japanese home islands. A bombing campaign would (and did) begin.
From the very start of the conflict in December 1941, the Japanese war plan had been to inflict such substantial losses on the allied forces so that the U.S. public would become war weary and the American government would be convinced to sue for peace and allow Japan to keep its conquests. A central element of the plan was Japan’s ability to project naval power through its aircraft carriers and battleships. However, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had suffered extensive air wing losses at aircraft carrier battles such as Coral Sea, Midway, and the Solomon Islands campaign of 1942–43. The losses were not only in aircraft carriers, but in skilled carrier pilots. After the Solomons campaign it took nearly a year for the IJN to reconstitute their air groups.
Early in the war the United States had only one operational aircraft carrier, USS Enterprise. By June 1944, Task Force 58 approaching Saipan included 7 fleet carriers and 8 light carriers with a combined fleet air group of 900 planes. The Japanese came to the conflict with 3 fleet carriers, 6 light carriers with a naval air wing of 450 aircraft – but with 300 land based aircraft on Tinian and Guam. Not only were the numbers in favor of the U.S. forces, but the capabilities of the U.S. pilots was, on the whole, vastly superior to their counterparts. This was due in part to the efforts of U.S. submarines sinking merchant oil tankers thereby limiting the aviation fuel oil available for training Japanese pilots. Some reports indicated that the average IJN pilot entered the battle with 200-300 hours of flying and with little to no combat experience. The average U.S. aviator had 800-900 hours of flying, much of it combat.
As before, there are plenty of online sources that detail the ebb and flow of the air campaign of Philippine Sea fought over two days. After the second day of the battle, IJN losses totaled three carriers, more than 350 carrier aircraft, and approximately 200 land-based aircraft – and their aircrews. In the five major “carrier-on-carrier” battles, from the Battle of the Coral Sea to the Battle of the Philippine Sea, the IJN lost nine carriers, while the USN had lost three. The aircraft and trained pilots lost at Philippine Sea were an irreplaceable blow to the already outnumbered Japanese fleet air arm. The Japanese carrier air groups lost 90 % of their force in two days. The Japanese had only enough pilots left to form a single air group for one light carrier.
Though still relatively unknown to general audiences of World War II history, the Formosa Air Battle (Oct. 12-16) was the single largest air-sea battle of the Pacific war. Japan committed a greater mass of air power to this battle—1,425 army and navy aircraft over the course of one week—more than anything the U.S. Navy had faced prior. In fact, the Japanese air force participating in the Formosa Air Battle was multiple times bigger than the carrier air formations encountered during the more well-known Battle of the Philippine Sea.
Overall the Japanese lost ~600 airplanes and crews. U.S. losses were 89 aircraft, however, almost all the U.S. pilots were rescued. Surviving Japanese pilots returned with tales of a stunning victory. It was reported that practically the whole U.S. Third Fleet had been sunk and the American carrier force was left in shambles with virtually all fleet carriers sunk.
The “victory” was celebrated by the IJA aviation wing, though the IJN command was initially skeptical of such reports. The “victory” narrative was carried forward by the military members of the cabinet until it reached Emperor Hirohito. He congratulated the Navy and Army for their success and declared a national holiday. Newspapers in particular trumpeted these claims, repeating that the U.S. task force was broken and in retreat. Even those unconvinced members of the IJN, up to and including Admiral Toyoda of the Combined Fleet, believed some kind of victory had been achieved off Formosa. It was trumpeted as the “decisive battle” envisioned in Japan’s war plan, Kantai Kessen (“Decisive Battle Doctrine”) – not to defeat Allied forces, but to bring the United States to the negotiating table.
Consider how this affects the problem for war termination. Virtually all wars end when one side realizes it has been defeated. From civilian to Emperor, there does not seem to be the realization their defeat is inevitable at this point – nor that the Allies are not interested in armistice or negotiated settlements. The Allies intend to win this war and prevent the next one.
A Sea Change in Naval Aviation Strategy and Tactics
This marked a shift from offensive Naval aviation operations as seen early in war to a purely defensive posture. With battle losses at Philippine Sea, the fall of Saipan, Tinian and Guam were only a matter of time. Japanese planners knew that the Allied forces would next focus on the Philippine Islands themselves. The Japanese military believed its only hope was to inflict such severe losses on the landing fleet that the Americans could be drawn into negotiations with the goal of leaving the Home Islands intact and still maintain control of some of the territories in East Asia, especially those key to import of critical raw materials.
From this situation was born the Kamikaze, “divine wind” (officially Shinpū Tokubetsu Kōgekitai – Divine Wind Special Attack Unit). They were a part of the Japanese Special Attack Units of military aviators who would fly suicide attacks against Allied naval vessels in the closing stages of the Pacific campaign of World War II.
The attacks began in October 1944 in the shadow of the losses at Philippine Sea. Japan had lost decisive battles key to their overall strategy. The corps of skilled aviators was decimated and replacements could not be trained fast enough. Japanese aircraft were becoming outdated with the introduction of new allied fighter planes. Japan had lost command of the air and sea. These factors, along with Japan’s unwillingness to surrender, led to the institutionalization of kamikaze tactics as a core aspect of Japanese air warfare strategy as Allied forces advanced towards the home islands.
In this atmosphere of strategic desperation, what appeared to the Western nations as erosion of psychological and doctrinal barriers to deliberate suicide was more likely a manifestation of the Bushido code. A tradition of death instead of defeat, capture, and shame was deeply entrenched in Japanese military culture – loyalty to the Emperor and honor until death. This was not limited to aircraft. In addition to kamikazes, the Japanese military also used or made plans for other Japanese Special Attack Units, including those involving Kairyu (submarines), Kaiten (human torpedoes), Shinyo (speedboats), and Fukuryu (individual divers).
Bushidō code and militarist ideology had long glorified death in service to the emperor. The loss at the Philippine Sea helped shift this from a theoretical ideal into military tactics.
The Battle of Biak Island, Peleliu, and the Battles of Philippine Sea and Formosa changed the nature of warfare in the Pacific.
Image credit: various photographs from Naval Aviation Museum, National World War II Museum, and US Navy Archives.