In the course of reading Scriptures you will often encounter the terms “Mt. Zion”, “Jerusalem”, and the “City of David.” Are the terms identical? Are they all actual locations? Do they carry symbolic meaning? Perhaps it is good to offer a brief post on what this all means.
Originally, Mount Zion referred specifically to the Jebusite fortress that King David conquered and made his capital (2 Samuel 5:7): “But David did capture the stronghold of Zion, which is the City of David.” The City of David is located south of what in our day is referred to as the “Old City” of Jerusalem, in a ridge area. The term “City of David” is often synonymous with the earliest settlement of what became Jerusalem.
In his efforts to unify all the tribes on Israel into one nation, David relocated the Ark of the Covenant to Zion indicating that God’s presence among His people was not centered on Zion and in the City of David: “The Ark was brought into the City of David with great rejoicing.” (2 Samuel 6:12-19). While David offered to build the Lord a “house,” construction of the Temple fell to David’s son, Solomon. The Temple was built on Mount Moriah, a part of the broader Zion area (1 Kings 8:1).
Zion is repeatedly described as a place of refuge and a symbol of God’s kingship over Israel (Ps 2:6). Today’s first reading holds the prophetic promise that the Law and the Word of the Lord will come forth from Zion, promising the possibility of divine wisdom and peace. “From Zion shall go forth instruction, and the word of the LORD from Jerusalem.” (Isa 2:3)
Zion is envisioned as the site of the Messiah’s reign, bringing justice and peace to all nations: “Rejoice heartily, daughter Zion… See, your king shall come to you.” (Zechariah 9:9) Zion is identified with the heavenly city, the ultimate destination of God’s faithful. In Revelation, the Lamb (Christ) stands victorious on Mount Zion with His redeemed people: “Then I looked, and there was the Lamb standing on Mount Zion, and with him a hundred and forty-four thousand.” (Rev 14:1)
There are several theological themes that are thus associated with Zion
- God’s Presence: Zion represents God’s dwelling among His people, through the Ark, the Temple, and ultimately through Christ.
- Redemption and Restoration: Zion is a symbol of hope, where God restores His people and fulfills His promises.
- Eschatological Hope: The heavenly Zion is a vision of eternal communion with God. In the New Testament, associated with the heavenly Jerusalem (Hebrews 12:22)
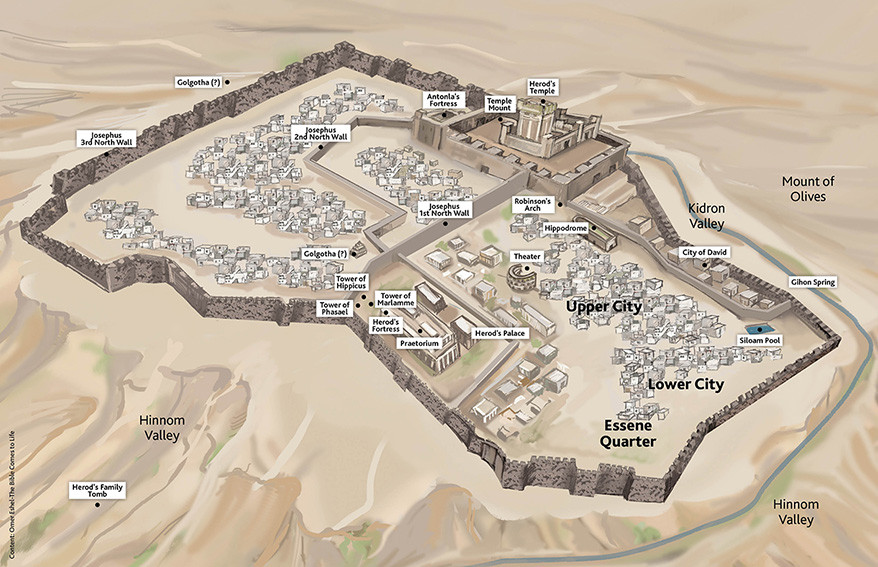
Where does Jerusalem fit into all of this? It doesn’t “fit it” but rather surrounds it all. As the capital of Israel grew, it outgrew the City of David and expanded to encompass the ancient settlement and Mount Zion. Jerusalem then took on all the historical and theological significance from both the City of David and Mount Zion and then served as the central city in biblical history and prophecy.
Discover more from friarmusings
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
